QMS Info
How Quality Management System (QMS) works in an organization and its main activities


- What is QMS?
- Quality Management System (QMS) is a formal system that documents processes, procedures and responsibilities for achieving quality principles and objectives.
- Goal: Increase customer satisfaction and continuous process improvement.
Introduction of QMS
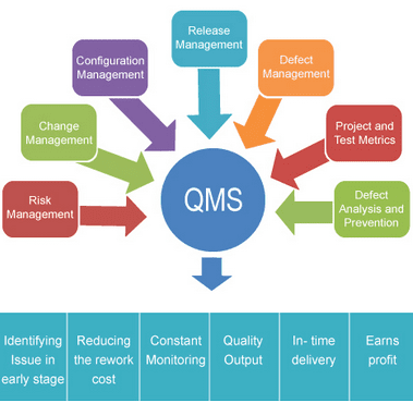
- Formulating quality policies and setting organizational goals.
- Process and Documentation.
- Regular audits and staff training.
- Identifying problems at an early stage.
- Error analysis and prevention.
- Customer complaints and feedback management.
Main Activities of QMS

A Quality Improvement Plan is an organization's framework for developing and improving processes. It includes essential information about how your organization will design, implement, manage, and assess quality.
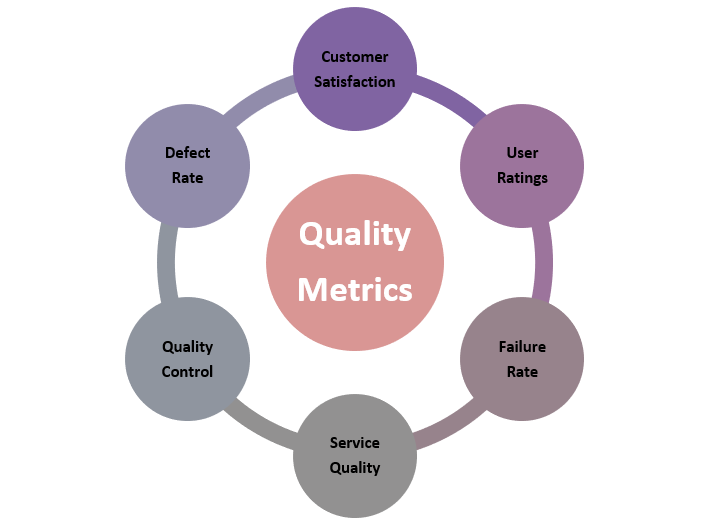

What is Quality Metrics?
Quality metrics are a key component of an effective quality management plan and are the measurements used in ensuring customers receive acceptable products or deliverables. Quality metrics are used to directly translate customer needs into acceptable performance measures in both products and processes.

- Manufacturing Sector: Ensuring quality at every step of the manufacturing process.
- Service Sector: Ensuring quality at every level of customer service.
- Healthcare: Quality is observed at every step of the treatment process.
- Economics and Banking: Transaction and Process Monitoring.
Sectors in which QMS operates
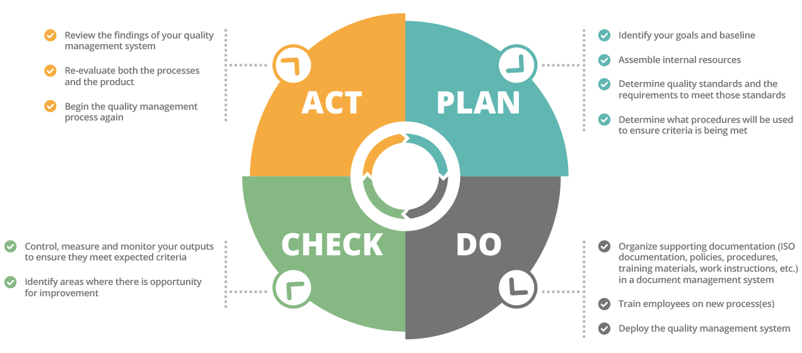
- Plan: Determining goals and procedures.
- Do: Conducting procedures properly.
- Check: Audit and analysis of activities.
- Act: Identifying problems and ensuring solutions and improvements.
How does QMS work?
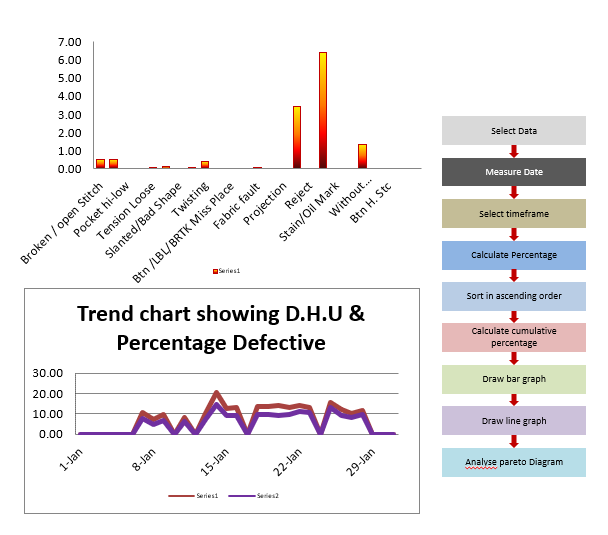
What Is Pareto Analysis?
Pareto Analysis is a technique used for decision making based on the Pareto Principle. Pareto Principle is based on 80/20 rule which says “80% of impacts are due to 20% of causes”. It emphasizes that a major number of issues are created by a relatively smaller number of underlying causes.
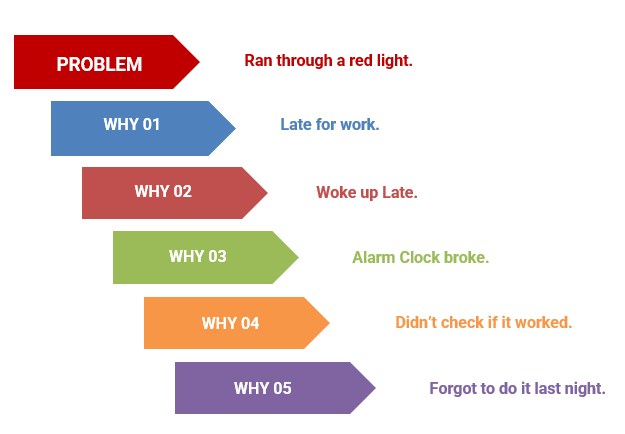
Origin of 5 Whys
The 5 whys method is part of the Toyoda Production System. Developed by Sakichi Toyoda, a Japanese inventor and industrialist. The technique became an integral part of the lean philosophy.
The basic of Toyoda's scientific approach to ask "Why" five times, each time directing the current "why" to the answer of the previous "why". The method asserts that the answer to the fifth "why" asked in this manner should reveal the root cause of the problem.

What is a Fishbone Diagram?
A Fishbone Diagram is also known as a “cause and effect diagram” or an Ishikawa Diagram (named after its inventor, Japanese quality control expert Kaoru Ishikawa).
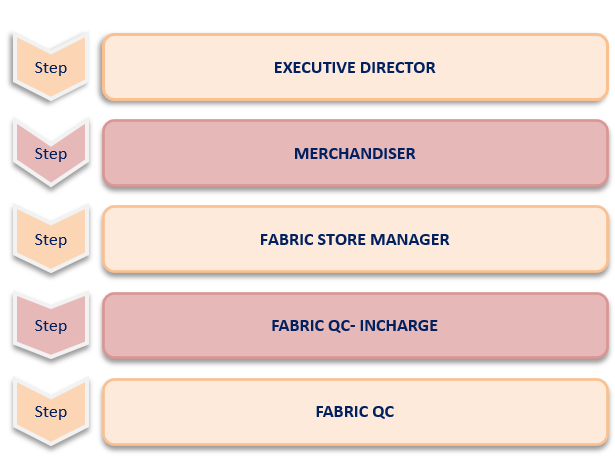
What is Escalation process?
The general meaning of the term escalation is the progressive increase in intensity or spread of a phenomenon – in this case a risk.
In the context of the project, the escalation process is generally a formal process to highlight the problem in question to a higher authority.
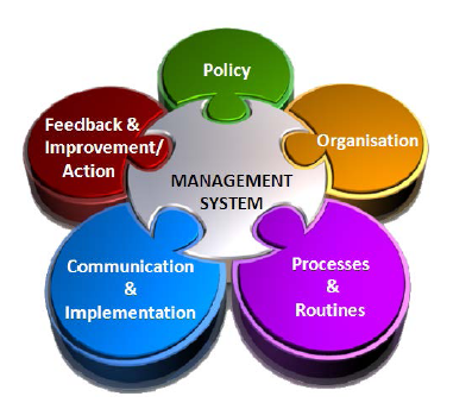
- Quality Policy and Goal.
- Process Control.
- Documentation and Record.
- Audit and Reviews.
- Continuous Improvement.
Elements of QMS

- Increase customer satisfaction.
- Increase effectiveness and efficiency.
- High quality products and services at low cost.
- Increasing the market competition of the organization.
Benefits of QMS

- Provide training to staff.
- Explain the importance of quality policy.
- Conduct regular audits.
- Maintain continuous improvement.
Tips for successful implementation of QMS